Moving beyond AI systems, such as ChatGPT that we have all become familiar with over the past few years, AI agents are designed to autonomously perform complex tasks by integrating decision-making, problem-solving, and interaction with various tools and environments. This enables agents to tackle multi-step challenges across a wide range of applications, from automating routine business processes to navigating intricate data analysis. Here at Qubika we build AI agents via our dedicated AI Agentic Factory – this article explains some of the work they are doing and outlines exactly what an agent is.
The progression from machine learning to GenAI, to now Agentic AI
We’ve witnessed the remarkable progression of AI, even just over the past few years. From Machine Learning (ML), where algorithms learned from data, we moved to Deep Learning (DL), which used complex neural networks for tasks like image recognition and natural language processing. This paved the way for Generative AI (GenAI), empowering AI to create new content, such as text and images, based on learned patterns. Now, with Agentic AI, systems can plan, use tools, and act autonomously to achieve complex goals, transitioning AI from content generation to independent problem-solving.
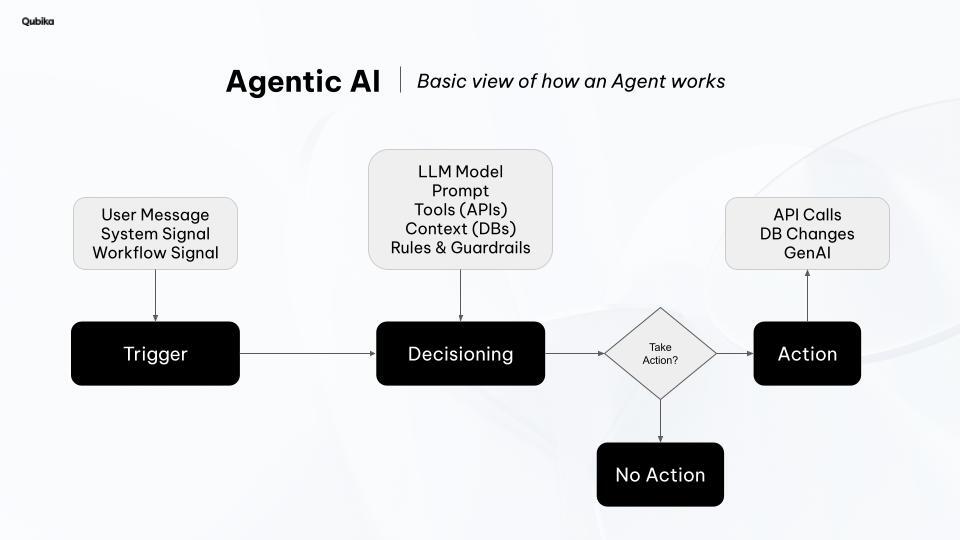
A basic overview of how an AI agent works
Understanding the process by which an AI agent works is an important first step to defining how they will most effectively benefit your organization.
The process is typically initiated by a “trigger”, which could be anything from a user query or a system alert to a specific workflow signal. This trigger then propels the system into the decisioning phase, where the core LLM-powered agent comes into play. Here, it processes the input by interpreting the prompt, leveraging external tools via APIs, drawing on contextual information from databases, and adhering to predefined rules and guardrails.
Based on this internal reasoning, the agent then decides whether to take action. If an action is warranted, the system proceeds to the action phase, executing tasks like making API calls, instigating database changes, or generating new content using its generative AI capabilities. This structured flow underscores how Agentic AI systems autonomously interpret inputs, evaluate using diverse resources, and execute intelligent responses.
One of the key differences to a traditional workflow is that the agent can determine the system or user’s intent in order to provide a custom, contextually-relevant, intelligent response. This contrasts with traditional workflows which would follow a predetermined, inflexible path.
Core building blocks of an AI agent
In summary, the core building blocks of an AI agent include:
- Goals & guardrails. Your data/ AI team will first define the agents’ objectives, constraints, and allowed tools. Agents then follow these guidelines.
- Perception & context. Agents gather state from user prompts, enterprise data, APIs, events, and prior memory.
- Planning loop. Agents decompose goals into steps, choose tools, and update plans as results arrive.
- Action & tool use. Agents can invoke APIs, run jobs, write to systems, or call other agents.
- Reflection & learning. Agents evaluate outcomes, retry, escalate, or fine‑tune behavior over time. This is a core difference to earlier RAG systems which didn’t evaluate responses.
- Observability & control. Logs, traces, replay, and policy checks allow enterprise teams to inspect and govern the effectiveness of the agent and control its behavior – thus ensuring compliance in highly regulated environments.
An AI agent vs an AI workflow: What’s the difference?
These are two key concepts in the design of AI systems. Put simply, an AI workflow is a structured sequence of steps or processes that an AI will use to achieve a specific outcome – think of typical task automation type activities – image tagging or document classification. An AI workflow could be used to classify incoming customer support messages for example.
On the other hand, an AI agent is a much more autonomous system that determines its course of action based on various inputs. It has a greater level of complexity than a workflow. Unlike a workflow, it doesn’t require step-by-step instructions, and instead will make decisions dynamically. An example of an agent would be a purchasing agent that can autonomously execute purchases based on the defined thresholds of a business.
Making it concrete: The example of the Qubika Finance Analyst AI Agent
One of the AI agents that Qubika’s Agentic Factory has built, is the Qubika Finance Analyst AI Agent which replicates the typical role of a data analyst in a finance department. We could see how traditional financial reporting, often manual and slow, struggles with the explosion of data in recent years. Even simple data cross-referencing could easily take a data analyst a full day, causing senior executives to wait days for crucial operational insights. Simultaneously, data professionals waste excessive time on data preparation rather than actual analysis, creating significant inefficiencies and delaying decisions.
Recognizing these challenges and the immense opportunity for innovation, we developed a specialized finance AI agent. Our goal was to revolutionize this common financial process by enabling rapid data extraction, analysis, and interpretation in seconds, not days or weeks.
It offers rapid analysis, retrieving and dissecting vast business data in seconds to accelerate insights. Crucially, it provides accurate, audit-friendly answers through cross-referencing and transparent “chain of thought” with source attribution.
Here you can read more about the finance agent and watch a demo of it in action.
The steps to building an AI agent: The role of platforms such as the Qubika Agentic Platform and Databricks Mosaic AI
Building an effective AI agent requires a methodical approach, transitioning from foundational components to sophisticated orchestration and deployment. This process typically involves several key stages, each significantly streamlined and enhanced by specialized platforms.
Here at Qubika we built the Qubika Agentic Platform to help businesses streamline the process of building agents – by having libraries and pre-built assets ready to go. To give an indication of the accelerated development times that such a platform can provide, we recently held Agentic Day, where our teams created 4 working agents in just 8 hours.
The Qubika Agentic Platform’s emphasis on security, adherence to best practices like OWASP, extensibility, and portability, provides a strong foundation for building scalable, enterprise-grade agents, even in highly regulated environments.
Complementing this, the Databricks Mosaic AI Platform also provides a strong option for businesses. It offers end-to-end capabilities across the entire AI agent lifecycle. From the initial stages of data preparation and feature engineering with its robust data management tools (like Unity Catalog for governance) to the critical steps of model building and fine-tuning, Databricks provides a unified environment. “Agent Bricks”, which it recently announced at the Databricks Data + AI Summit earlier this year, is designed to specifically aid in building data-grounded agents, while tools like AI Gateway ensure consistent data governance and guardrails for GenAI deployments.
Closing: AI Agents are already driving significant change
To answer the question, “what is an AI agent” – we need to look at how they are already driving significant change in enterprise environments – building on the progress we’ve seen in earlier years with machine learning, deep learning, and GenAI. As exemplified by the Qubika Finance Analyst Agent, they deliver ROI because they have the ability to determine intent – and thus can fundamentally transform and accelerate current business processes. Platforms like the Qubika Agentic Platform and Databricks Mosaic AI are crucial in simplifying and accelerating their development and scalable deployment. Embracing Agentic AI is a clear path for enterprises to unlock new levels of efficiency, intelligence, and competitive advantage.
Ready to explore what an AI agent can do in your organization?
AI agents are designed to autonomously perform complex tasks by integrating decision-making, problem-solving, and interaction with various tools and environments.


























